Relationship between olive cultivation and olive oil quality
From the olive grove to the glass
The quality of an olive oil is not just created during pressing. The conditions under which the olives grow, ripen and are harvested are much more decisive. Climate, soil, variety and harvesting practices have a significant influence on taste, stability and nutrient content. If you really want to understand olive oil, you have to start with olive cultivation.

Olive cultivation worldwide – a brief overview
Origin and production areas
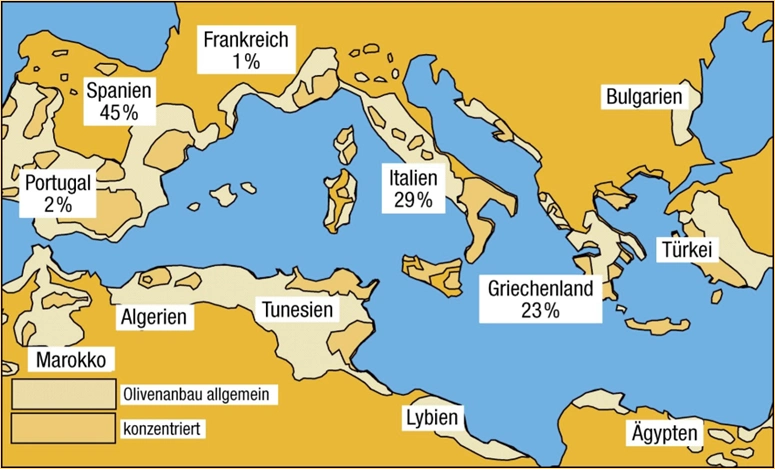
Olive trees grow predominantly in the Mediterranean region. Within the European Union, there are several hundred million olive trees, which supply a large proportion of the world’s olive oil. Countries such as Spain, Italy and Greece shape the global market, as do non-European producers.
Climatic conditions
The olive tree is robust, but reacts sensitively to extremes. Negative effects on fruit development are caused by:
- long periods of drought
- heat stress during ripening
- heavy rainfall at the wrong time
- unstable weather patterns
Such factors can reduce yields and impair the sensory quality of the oil.
Comparison of cultivation systems
Classic olive cultivation
- widely spaced trees
- manual care and harvesting
- low mechanization
This form of cultivation is labor-intensive, but can produce very distinctive oils.
Modern intensive cultivation
- denser planting
- targeted irrigation
- partially mechanized harvesting
It combines efficiency with controlled quality, but requires experience and precise planning.
Super-intensive olive cultivation
- Espalier shapes
- fully mechanized harvesting
- high yields per area
Economically attractive, but dependent on variety, location and sustainable management.
Soil, variety and care as quality factors
Importance of the soil
Soil condition and nutrient supply influence:
- Fruit size
- Oil content
- Ripening speed
Healthy soil is the basis for high-quality olives.
Variety of types
There are hundreds of olive varieties worldwide. Each variety develops its own aroma profile and reacts differently to climate and harvest time. The choice of variety is therefore a conscious quality decision.
Tree care and plant health
Regular pruning, pest control and balanced fertilization are crucial. Diseases or pest infestations have a direct negative impact on olive oil quality.
Harvest time and organization
Ripeness of the olives
The time of harvest influences:
- Bitterness and pungency
- Aroma intensity
- Polyphenol content
Harvesting too early or too late can disrupt the sensory balance.
Logistics after the harvest
The handling of the olives after picking is just as important:
- short distances to the oil mill
- air-permeable containers
- fast processing
Long storage times or incorrect storage conditions lead to a loss of quality that cannot be reversed.
Conclusion: Olive oil quality begins in the olive grove
The influence of olive cultivation on olive oil quality is decisive. Climate, cultivation system, care and harvesting determine the basis for a high-quality oil. Only when these factors are right can an olive oil be produced in the mill that is sensorially convincing and retains its health value.